API Signature Verification
This document introduces how to use the API signature and verification mechanism to ensure the security and integrity of API requests.
1. Obtain API Key and API Secret
Refer to the Intergrate Merchant API document to obtain the API Key and API Secret.
2. RESTful Request Signature
2.1 Request Headers
All RESTful requests need to include the following parameters in the headers:
- X-PAY-KEY: The API Key in string format.
- X-PAY-SIGN: The hash value generated by the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm, encoded in Base64.
- X-PAY-TIMESTAMP: The Unix timestamp of the request, in seconds, in string format, such as
'1684304935'. To prevent replay attacks, the difference between the timestamp and the server time cannot exceed 1 minute.
Note: All POST requests also need to include the Content-Type: application/json parameter in the headers and ensure that the request body is valid JSON.
2.2 Signature Generation
The X-PAY-SIGN request header is generated by the API Secret and the request parameters. The steps to generate the signature are as follows:
- Concatenate the request timestamp
timestamp, request methodmethod(GET, POST), request pathrequestPath(excluding the domain), and request bodybodyinto a stringtimestamp + method + requestPath + body. - Use the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm, with the API Secret as the key, to hash the concatenated string.
- Encode the hash value in Base64 to get the value of X-PAY-SIGN.
Below is an example of generating a signature using JavaScript:
import crypto from 'crypto';
const timestamp = '1684304935';
const sign = crypto.createHmac('sha256', apiSecret)
.update(timestamp + 'GET' + '/api/mer/conf/list/currency?chainId=101')
.digest('base64');
Where,
apiSecretis the API Secret;timestampis the Unix timestamp of the request, in seconds, the same as the value ofX-PAY-TIMESTAMP;GETis the request methodmethod;/api/mer/conf/list/currency?chainId=101is the request pathrequestPath, i.e., thepathname+searchpart of the URL (for GET requests, it includes the query parameters);bodyis the request body. For GET requests, it is empty. For POST requests, it is the JSON string of the request body, such as{"chainId":101,"description": "some products","isLegalTender": 1,"notifyUrl":"https://some-notify-url.com","outTradeNo":"12345","quoteAmount":"11.22","quoteCurrencySymbol":"USD"}.- The obtained
signis the value ofX-PAY-SIGN.
2.3 Signature Example
- Java
- PHP
public void getSignature(String requestPath, String body, String method) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
String apiUrl = 'API Request Domain';
String apiKey = "your-api-key";
String secret = "your-api-secret";
// Assemble the signature content
StringBuilder sign = new StringBuilder();
// Timestamp
String timestamp = String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
sign.append(timestamp);
// Request method
sign.append(method.toUpperCase());
// Request path
sign.append(requestPath);
// Request body as a JSON string
sign.append(body);
// HMAC SHA256 encryption
Mac sha256Hmac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "HmacSHA256");
sha256Hmac.init(secretKeySpec);
byte[] hmacBytes = sha256Hmac.doFinal(sign.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String apiSign = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(hmacBytes);
// Send the request
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
// Set request headers
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
headers.set("X-PAY-KEY", apiKey);
headers.set("X-PAY-SIGN", apiSign);
headers.set("X-PAY-TIMESTAMP", timestamp);
HttpEntity<String> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(body, headers);
// Request URL
String url = apiUrl + requestPath;
// Send the request and get the response (here is a post request)
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.POST, requestEntity, String.class);
}
<?php
class Signature
{
const API_URL = 'API Request Domain';
const API_KEY = 'your-api-key';
const SECRET_KEY = 'your-api-secret';
public static function request($requestPath, $params, $method)
{
if (strtoupper($method) == 'GET') {
$requestPath .= $params ? '?'.http_build_query($params) : '';
$params = [];
}
$url = self::API_URL.$requestPath;
$body = $params ? json_encode($params, JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES) : '';
$timestamp =time();
$sign = self::signature($timestamp, $method, $requestPath, $body, self::SECRET_KEY);
$headers = self::getHeader(self::API_KEY, $sign, $timestamp);
$ch= curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
if($method == "POST") {
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $body);
}
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, $headers);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER , FALSE);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST, FALSE);
$return = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$return = json_decode($return,true);
return $return;
}
public static function getHeader($apiKey, $sign, $timestamp)
{
$headers = array();
$headers[] = "Content-Type: application/json";
$headers[] = "X-PAY-KEY: $apiKey";
$headers[] = "X-PAY-SIGN: $sign";
$headers[] = "X-PAY-TIMESTAMP: $timestamp";
$headers[] = "Expect: ";
return $headers;
}
public static function getTimestamp()
{
return date("Y-m-d\TH:i:s"). substr((string)microtime(), 1, 4) . 'Z';
}
public static function signature($timestamp, $method, $requestPath, $body, $secretKey)
{
$message = (string) $timestamp . strtoupper($method) . $requestPath . (string) $body;
return base64_encode(hash_hmac('sha256', $message, $secretKey, true));
}
}
3. Test Request
On each API reference page, we provide a request trial panel for interface testing:
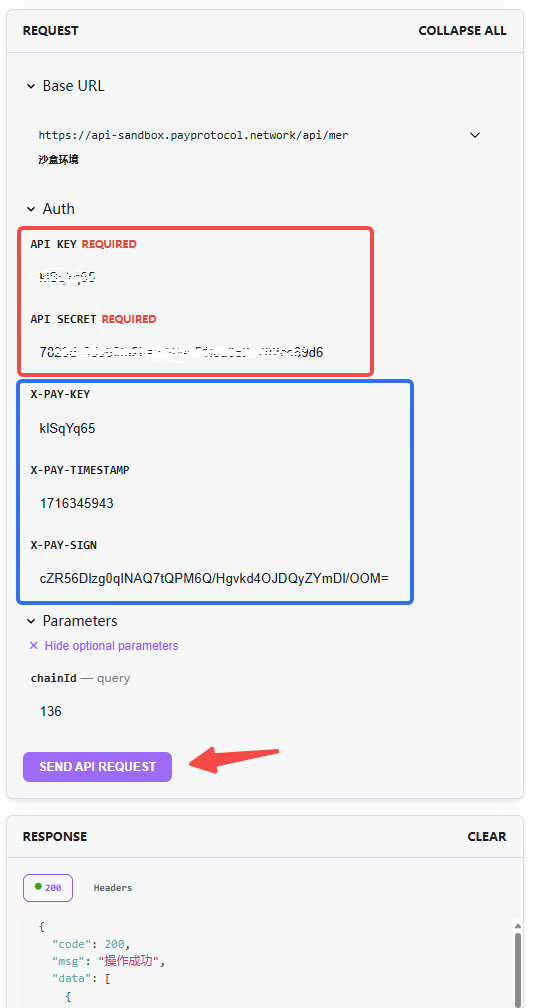
In the trial panel, you must enter the API Key and API Secret, then fill in the request parameters. The panel will automatically generate the three headers required for the signature. Click the "SEND API REQUEST" button to send the request and view the response below.
You can select the BaseURL for testing in different environments. The sandbox environment and the production environment are two separate systems, please distinguish when using. The merchant you registered in the sandbox environment cannot be used in the production environment, and vice versa.